5 Types of Cybercriminals and How to Protect Against Them

[MUSIC PLAYING]
(DESCRIPTION)
This content is brought to you by Travelers. The Travelers Umbrella logo. Text, 5 Types of Cybercriminals.
(SPEECH)
SPEAKER: When it comes to protecting your business from a data breach, you'll want to be on the lookout for a new kind of criminal, the cyber kind. They can be tough to spot, but if you can recognize these five common cybercriminal threats, you just may save your organization from a costly but preventable cyberattack.
(DESCRIPTION)
Graphic of a computer is shown. Next image is a skull on a computer screen. Binoculars appear above the image of a graphic of a figure's head in a hood behind a computer screen. A magnifying glass appears with the image of a computer and figure’s head in a hood in it. A sketch image of three people at a desk behind computers appear. Next image, skull and crossbones on a computer stick out of an envelope.
(SPEECH)
Number 1, the social engineer. Cybercriminals fake an identity and request data-rich, information, like a filled-out tax form, frequently in a time-pressured scenario.
(DESCRIPTION)
A clip board that says TAX on it appears. An arrow moving in a clockwise motion appears. A fishing hook winds into a computer screen with a textbox with the word "Password" above it. Sketch images of documents appear on the screen. A triangle image appears with a skull and cross bones in the center of it. Dollar signs appear in the form of stacking money.
(SPEECH)
Number 2, the spear phisher. These thieves send malicious emails altered to appear legitimate, containing links that unlock access to banking credentials, trade secrets, and personal information. Number 3, the hacker. Most confirmed data breaches are the result of hackers leveraging weak default or stolen passwords.
Number 4, the rogue employee. Current or former disgruntled workers can abuse their insider access and knowledge. Number 5, the ransom artist. The growth of ransomware as a service makes it easier for bad actors to seize control of data and force businesses to pay them or else.
To learn how to defend against these cybercriminals, visit travelers.com.
(DESCRIPTION)
The Travelers Umbrella logo. Text, Text, Visit travelers.com. Copyright 2018, The Travelers Indemnity Company. All rights reserved. Travelers and the Travelers Umbrella logo are registered trademarks of the Travelers Indemnity Company in the U.S. and other countries.
Understanding the types of cybercriminals and their techniques can help protect your organization from a data breach. Here are some common threats and steps a business can take.
1. The Social Engineer
Cyber criminals pretending to be someone else can trick unsuspecting employees to compromise data. In one scenario, a spoof email purporting to be from the CEO of the company directs an employee to send a PDF with employees’ 1099 tax forms for an upcoming meeting with the Internal Revenue Service. The social engineer is able to capture Personally Identifiable Information (PII).
“We often see people making mistakes like this,” said Jennifer Coughlin, a partner at Mullen Coughlin LLC, a data breach law firm that works with Travelers Insurance. “Encourage employees to make a phone call and speak to the person, instead of leaving a voicemail, to verify all requests for sensitive, confidential or protected information and financial information before they reply with the requested information. Employees should also ensure the 'reply to' address is, in fact, the email address of the requesting employee and send this type of information via an encrypted email message.” Beware time-sensitive requests, as social engineers sometimes use a sense of urgency to compel victims into unsafe behavior.
2. The Spear Phisher
Social threats factored into just under one-third of confirmed data breaches, with phishing the tactic used in 92% of social-related attacks.1 An email can appear to be from a legitimate sender but actually contain a malicious attachment or link that can give spear phishers access to banking credentials, trade secrets and other information that they are able to access.
“Companies can have employee training that both prepares and tests employees to recognize and respond to malicious phishing attempts,” said Tim Francis, Travelers Enterprise Cyber Lead. If a phishing attempt is successful, having the proper security in place provides another line of defense: protecting the rest of your network by segmenting the network and implementing strong authentication between the network and important data.
3. The Hacker
Nearly two-thirds of confirmed data breaches involved leveraging weak, default or stolen passwords.2 Malware poses a serious threat, as it can capture keystrokes from an infected device even if employees use strong passwords with special characters and a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters.
Still, strong passwords are the first line of defense against hackers, according to Francis. “Use multifactor authentication, enforce strong password requirements, patch operating systems, software and apps, and increase redundancy and bandwidth,” Francis said.
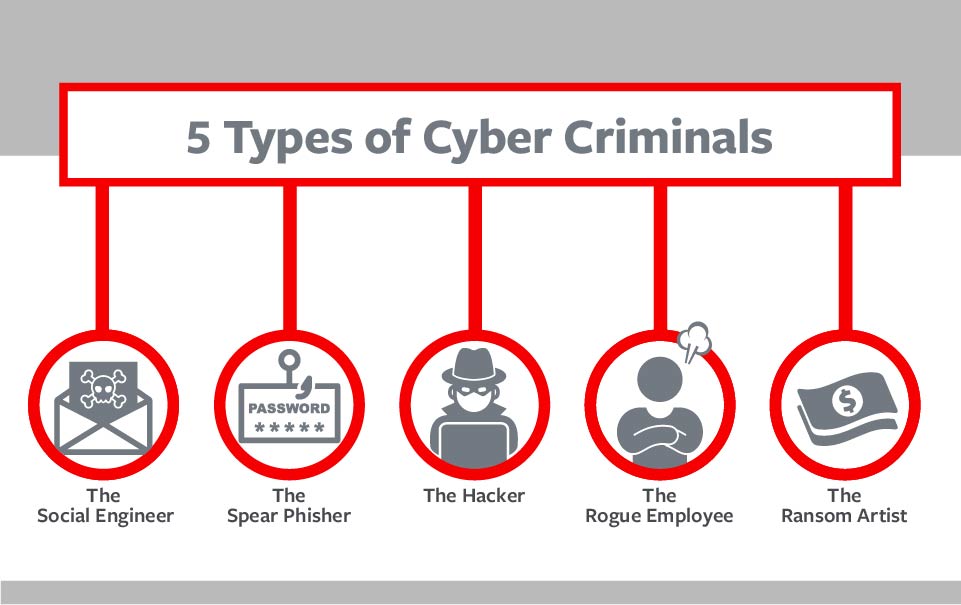
4. The Rogue Employee
Disgruntled employees present an insider threat to data. Insider threats accounted for 15% of breaches across all patterns,3 and they can be especially challenging for companies because employees often have both access to data and knowledge of what is stored and where.
Restricting access to sensitive data to only employees with an immediate need to use the data can help reduce the threat. Companies can limit, log and monitor internal account usage to protect against rogue employees, as well as protect against external attackers disguising themselves as legitimate users.
5. The Ransom Artist
Bad actors have been modifying codes and implementing new ransom attack methods, sparking a rise in ransomware as the fifth most common form of malware, up from the 22nd most common in the 2014 Verizon Data Breach Incident Report.4 Many companies are paying ransom, often via anonymous bitcoin payments, to have their data restored.
“The people who fall victim to ransomware are not following the information security rules, including encryption and frequent backups,” said Pascal Millaire, Vice President and General Manager of Cyber Insurance at Symantec. If you are able to independently restore the data, you will be less affected by the ransom attempt, but you will still need to determine how the cyber thief gained access to your network before making their ransom attempt.


