Connected Manufacturing: The Technology Behind IoT
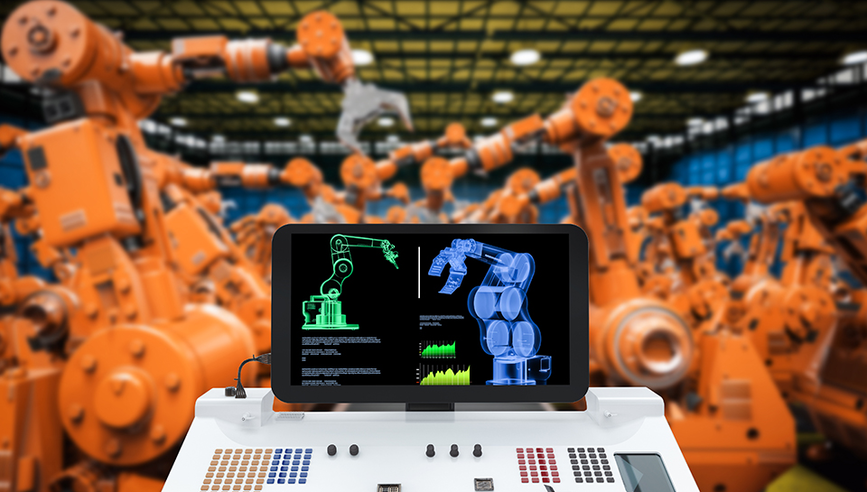


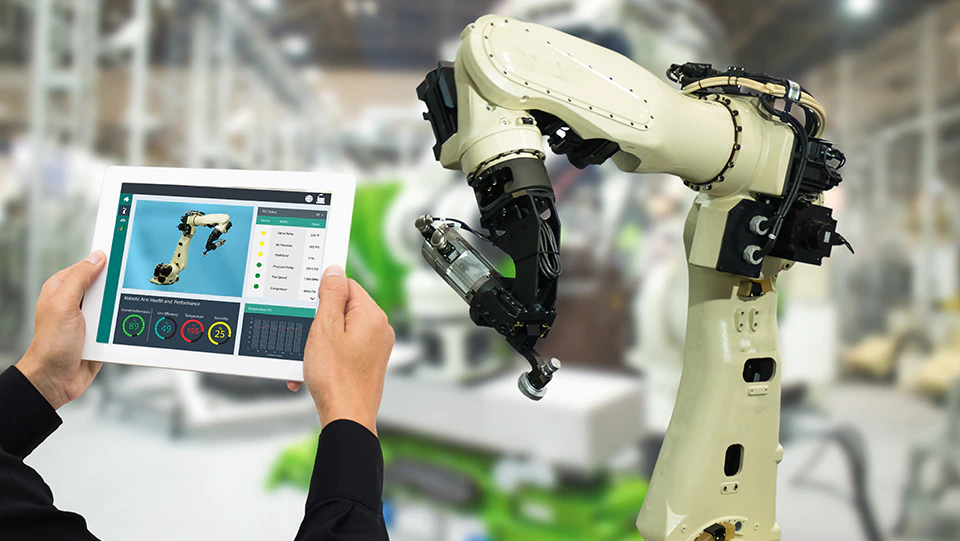
Many manufacturers are adopting new technologies to improve productivity, efficiency and reliability. Examples include robotics, networked communication systems, sophisticated sensors and actuators, software applications to conduct robust data analytics and autonomous machine to machine communications. The technology driving this revolution has been called the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). Here are four elements manufacturers need to consider.
- Devices. The sensors that collect data about the environment, and the actuators that operate machines, turn valves, energize motors and a variety of other actions needed to make “Smart Manufacturing Plants” run.
- Communication. The communication networks that allow the devices to communicate to each other, to the cloud or to someone’s mobile device. The Internet is the backbone for this communication and allows for virtually unlimited connections and communications across the globe.
- Data Storage. The data collected by the connected sensors needs to be stored for analysis in real time or sometime in the future. Data can be stored locally or in cloud servers with extensive capacity for storage and scalability.
- Data Analytics. Computer algorithms – even artificial intelligence (AI) – interprets stored data for actionable insights, such as performing predictive maintenance on equipment, helping to place orders for raw materials or to monitor customer trends over time.
As the technology tools available to manufacturers become more complex and interconnected, manufacturers will need to ensure safeguards are in place to mitigate risk at every point where data is gathered, stored and shared.